What to do if your page isn’t growing? This is a question that concerns many website owners and SEO specialists. But in reality, every problem has a solution, so instead of panicking, let’s read the advice of top website promotion specialists.
In this article, we will look at the most common reasons for problematic pages that cannot achieve the positions we expect from them.
Checklist: what to check if your page isn’t growing
Most often, a page does not rank at the top of search results not because of Google updates or complex algorithms, but simply because the basics of SEO have not been implemented. So, here is a standard plan of action if your page is not climbing the rankings.
Measure page load speed
Google recognized page load speed as one of the factors affecting website rankings back in 2010. And the ultimate updates only confirm how much speed determines your Page Experience.
You can take the easy route — go to the site, and if the loading speed is acceptable to you as a user, then everything is fine.
If it is visually clear that the site is loading very slowly, then we measure the speed of the site from desktop and mobile devices. This can be done using Google PageSpeed Insights (Core Web Vitals metrics) or Pingdom Tools
Note that the loading speed of your pages is affected by the choice and location of the data center where you host your website files. Therefore, you should take a responsible approach to choosing a host.
If you are looking for truly fast hosting, choose NVMe Hosting from HostPro. Thanks to the successful combination of high-performance processors and NVMe drives, websites are accelerated by 8 times, which, of course, affects the ability to reach the top of search results.
Analyze the niche and user intent
Proper niche analysis should take place before page optimization. First of all, pay attention to the type of page — is it a product, blog page, or service? Your page type should match the types of similar pages in the search results, as well as the content blocks available on them (for example, an application form, price table, or review block).
You should also check whether your text will really be more useful to users than that of your competitors in the top search results, and whether your content really meets the expectations of your audience. Or, in SEO terms, whether the content of the page matches the user’s intent. To do this, simply look at your pages through the eyes of a user.
Another option is to check GA4 (Google Analytics 4) to see how much time users spend on the page. If you see that a user was on the site for only a few seconds (a rather subjective value), then there is definitely something wrong with the content on the page.

If users visit your page and realize that it is not what they expected to see there, it is natural that the bounce rate will increase. And if there are too many such sessions, the search engine will lower the page’s ranking and it will drop in the search results.
This also includes compliance with the E-E-A-T concept (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness), which you should definitely pay attention to if your project is content-based and focused on YMYL topics – “Finance,” “Health,” and “Safety.”
Checking the technical component
The next step is to wait for technical readiness and, possibly, technical malfunctions of the page in Google Search Console. It is better to check using a proxy or VPN service to see the availability of the server from different points around the world.
So, let’s see:
- what is the status code (HTTP server status, there may be 400 or 300 errors);
- is the page indexed, you may just need to wait for Google to index it;
- what the page looks like when rendered by a search bot — to do this, after checking the URL in GSC, click on the right side of the screen and see how the search robot processed the document. Then you can copy this code into any graphics editor and check it for correctness.
At this stage, we also check whether this page is in Google’s cache and how it looks in the search engine’s “understanding” — to do this, enter the operator cache:URL-page without spaces in the search. We visually compare the content and the page in the cache (what Google sees) and not in the cache (what the user sees).
If there is no cache, Google may not have had time to form it yet.
Generate a report on the mobile version of the page
In Google Chrome, go to the URL you want to check, open Chrome DevTools (“Developer Tools”), which can be done by pressing F12. Go to the ‘Lighthouse’ tab ⇨ click the “Analyze page load” button.
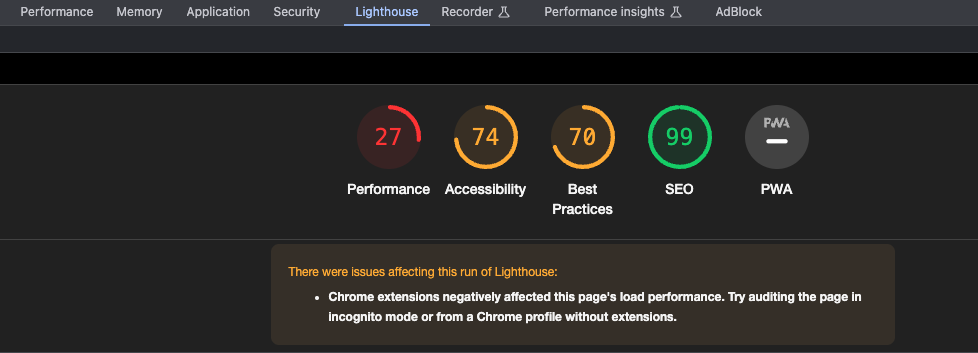
And we receive a free report on performance, availability, and SEO.
Examine the quantity and quality of links
Using Ahrefs or Majestic , we check the external link weight (link juice), namely the URL rating (UR) indicator, to understand the strength and authority of our page and our competitors’ pages. After all, the number of links is not always indicative; the main thing in this story is the trustworthiness and traffic of donor resources.
You can have 200 cheap backlinks from forums, but whether this will be beneficial for promotion is debatable.
Of course, our page should have at least the same number of external links as our competitors on average for five keywords. But again, remember that links from certain sites can only hurt you:
- illegal and untrustworthy resources;
- sites that are banned from advertising on Google Ads;
- broken sites;
- donors that already have too many links to sites of different orientations. This indicator can be measured in such a way that the number of outgoing links from the domain should not exceed the number of incoming links. This data can be obtained from Ahrefs. However, if a resource receives a lot of traffic, overspam can be considered normal;
- sites with very low or zero traffic.
And if, as a result, we still see the same anomaly, with both us and our competitors having 20 external links, but the URL rating of our page remains lower, then it is better to move away from the strategy of “filling” links and do the following.
Namely, use internal intermediary pages—build links to pages that refer to our problematic page. For example, if the problem is with a category page, we take blog pages or product pages that refer to our category page.
Presence of keywords
Check if the keywords are really in your content. It is better to place the main keywords in the Title and H1, and the secondary ones in the H2, H3 headings and directly in the text, lists, tables, and anchors of outgoing links. It does not have to be an exact match of the keyword; you can conjugate and separate words. The main thing is that it reads organically.
It is also important not to overdo it with the number of keywords, because then it will be spam, and the page may not appear in the search results again. You can check the page for spam at copywritely.com.
We will also add brand keywords to this section. You can check, for example, in Serpstat or Similarweb , how many brand queries your competitors rank for, how often they are searched for by brand name, and compare this with your situation. If the company is still unknown and people are not yet searching for it by brand keywords, you can focus on getting more people to write about you on the internet. This includes reviews.
It is clear that it is much more difficult for a newly launched website to gain positions, but if Google at least associates your website with your brand name, that is already a good start. You can check this as follows: if you are first in organic search results for your brand name, everything is fine, and if there are 2-6 more sublinks after your main link, that’s great.
Anchor list
If your anchor list contains more than 80% of identical commercial anchors (link texts) with exact keyword usage, this can also lead to a drop in rankings. In this case, you will need to rework your anchor list so that there is minimal repetition. You can check your anchor list on Ahrefs, in the “Anchors” section.
In general, it is desirable that each link from an external site corresponds to a single commercial anchor, i.e., ideally, they should be unique.
Following this logic, if we want to promote the query “buy a grill,” then the one link that corresponds to this anchor should be from the most authoritative and powerful donor site. And the scheme is, in fact, as simple as pie — we take queries from Google Search Console and build unique anchors based on them.
Here, we do not take into account branded anchors and our internal links, for example, from our blog to a product page. In principle, there are no restrictions on repeating anchors, even commercial ones, within your site.
If nothing helps
You can take more radical measures.
Nofollow or Canonical
If we have a product page that is not promoting well, we may think, “Maybe we should delete it and start over?” But that’s not a very good solution. Instead, you can try putting a nofollow tag on it and placing the page itself in “Similar Products” on the page that is already at the top.
Also, if there is a more advanced page with a similar product, you can set a canonical tag and thus send Google a signal about the better page that you want to show to users. And then add the problematic page to “Similar Products” again.
Satellite site and 301 redirect
In particular, the situation can be fixed by creating a small satellite site with a domain that exactly matches the keyword and working on external links to it. Then it should be left to “settle” for 1-2 months, after which it will be possible to make a 301 redirect to the site we need.
Buying a competitor’s site and redirecting
You can also find a website in the top 10 or at least on the second page of search results for your queries, offer to buy it from the owners, and then redirect it to your own website. It is quite likely that someone may get tired of running this particular business, and by redirecting from an already promoted competitor’s website, you can significantly boost your position.
To do this, you don’t have to search for such sites yourself, you can simply actively browse bulletin boards where people want to sell a business or domain, or use a domain backorder service, which automatically registers domains after they become available.
Automatic interception of newly released domains is now available in HostPro. You can pre-order the desired domain in the Ukrainian zone in your Personal Account. You can read more about the backorder here.
Changing the page URL
Alternatively, if even after all optimizations the page remains in the 20th or 30th positions, then you can consider changing the URL without a redirect. Perhaps this URL has accumulated so many negative signals that the only way out is to reset the page rating.
Indexing a page on a test domain
Check if Google has indexed the page from the test domain and considers the one on the main site to be a duplicate.
In conclusion
Let’s also pay attention to the following case: if a page cannot rank high in SERP for a single query, you can cut this keyword out of the content and create a separate page for it.
So, let’s summarize what to check and analyze if a page is not moving to the top:
- loading speed (in particular, server response time – TTTB);
- analysis of the niche and types of pages at the top;
- user intent relevance;
- content blocks on competitors’ pages and on our page;
- technical errors in Google Search Console;
- mobile version performance;
- quality and quantity of backlinks, anchors;
- keys and spam;
- E-E-A-T compliance, if the project is content-based.