Due to hosting, we can access and admire websites we regularly go to. Some sites use VPS hosting, as their owners know how VPS works. The last thing you want is to fall behind by not knowing what it is and whether you need to use VPS. In this article, we offer a beginner’s guide on VPS service and provide a comparison with other hosting services as well as point out how to choose a VPS web host. No time to lose, so read on!
What is VPS?
VPS stands for a virtual private server. Let’s break the definition down in the following way to better understand what VPS actually is.
In the VPS definition, a server means a powerful type of hardware where every file and all the data is stored. By files and data, we mean a website, because that’s what a website consists of, namely files and a database.
Private denotes that the server space belongs to a single user and there are no other users sharing the same space.
Virtual means that the server we just talked about is split into several virtual machines. These virtual machines create segments of space on a single server. These segments are occupied by websites that are hosted on the server. Most importantly, the websites reside independently from one another.
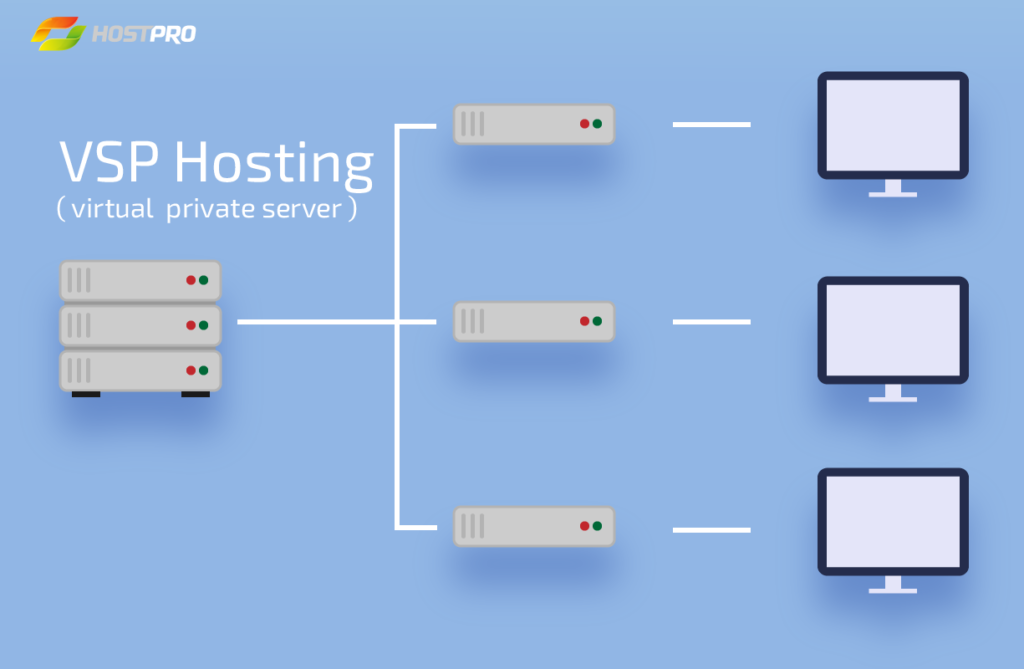
How can VPS be compared to other types of hosting?
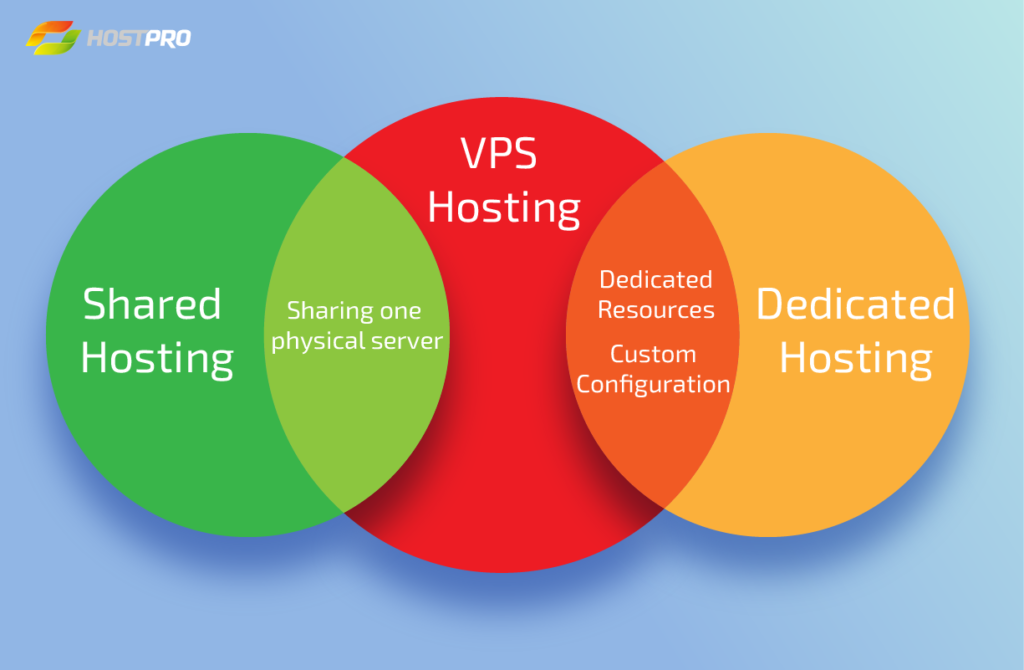
Basically, hosting most often involves servers that can be configured in different ways by a host. There are two hosting types that VPS can be compared to: shared hosting and a dedicated server. VPS has become a symbiosis of the two.
To understand how VPS combines the shared hosting option and a dedicated server, let’s see what similarities they bear.
When a user purchases a hosting plan, the resources they really purchase include:
- storage
- CPU cores
- memory (RAM)
- bandwidth (it should be unlimited)
With shared hosting—which is the most highly sought option by new website owners—a user buys the space on the server. The tricky thing though is that the user shares this space with others. In other words, the resources are distributed among all the users on this single server.
A dedicated server is one single server that is allocated for one user. All the resources like storage space, CPUs, RAM, and bandwidth belong to one user only. This is a rather expensive option as compared to shared hosting. However, with a dedicated server, the user has total control over the resources and has the freedom to customize the software the way they want.
So where does VPS stand? Right in between!
When buying a VPS package, the user will share the server with other websites (just like with shared hosting). But the websites hosted on the server have their own virtual compartments, which bear resemblance to a dedicated server.
VPS is a preferred option for those who have budget constraints but still can benefit from the isolation VPS offers.
Let’s get to the bottom of this and see how come one server lets the websites reside independently from one another.
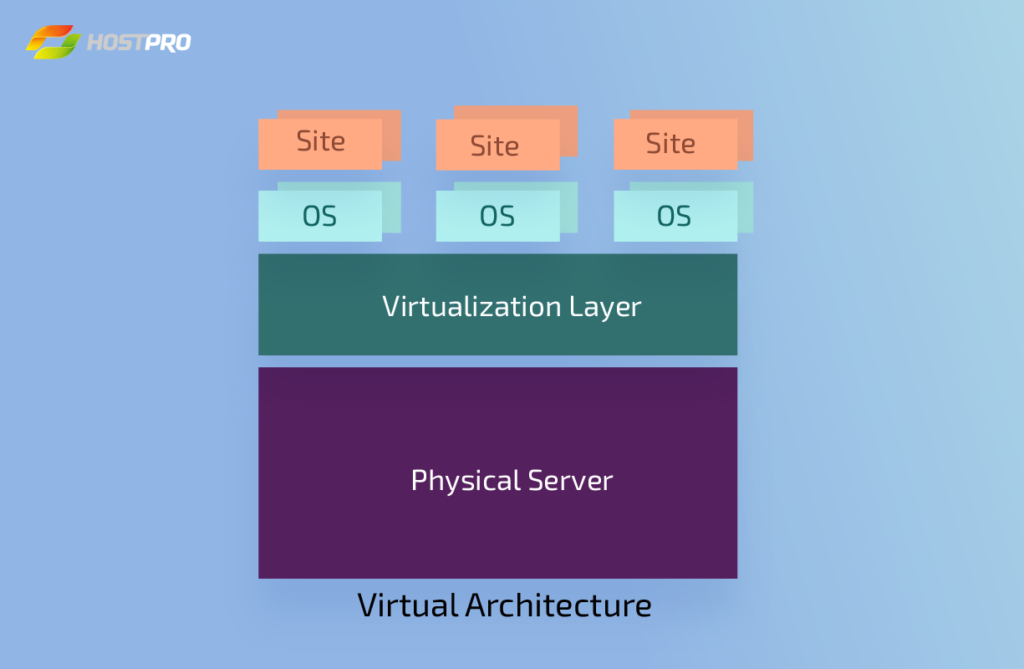
VPS: How does it work?
VPS servers have a complex architecture known as virtual architecture. We have bare metal (the server) and a virtual layer placed over the server. The virtual layer also called a hypervisor (the tech term for the virtualization layer) pools the resources together creating virtual segments where separate websites can be allocated. The virtualization layer allows the user to place any operating system and use the resources given for the segment. In other words, it’s called KVM virtualization.
VPS hosting provider: How to choose the best one
Upgrading to a VPS plan can be a daunting task if one doesn’t know where to begin, especially when choosing from a variety of companies. There are key features to consider. We lay out the essential ones.
Uptime
Each company should be able to provide clients with an uptime guarantee. It’s worth checking what a host offers in terms of uptime and then finalize the decision. Uptime means a lot for a website, letting it stay online practically all the time (unless there’s scheduled maintenance works). The better uptime a provider can offer, the more chances there are that the customers will reach the website.
Managed or unmanaged server
If the client has the technical know-how they may choose the unmanaged VPS. In the case when the user has little to no technical background, the provider takes care of the server related issues. The provider is responsible for setting up, configuring, and upgrading the server. With the managed option, the user is free to devote all their time to the website instead of taking care of the server and website protection.
Customer support
A VPS hosting provider should offer 24/7 support coverage. The tech team behind the server should have a well-designed ticketing system to solve day-to-day issues that may come up. For instance, any decent customer support should be able to:
- Install SSL and configure the work through HTTPS
- Compile a server with the optimal configuration
- Create backups
- Retrieve website copies
- Transfer sites safely
- Tune the necessary plugins
- Optimize website speed on the server end
- Select, install & tune OS
- Update OS and package base as a whole
- Install a control panel
These and many more tasks are executed by the customer support to lift all the care off the website owner’s shoulders.
Backups
A reliable web hosting company should provide backups in order to retrieve data or files in the time when the website fails to perform. The user should look into the backup policy a company has. It is critical to know how often backups are made and how long each copy is stored. It’s vital that the copy be stored on a separate server. If something happens with the server a website is placed on, the website owner can easily retrieve the latest website copy.
Operating system
Another key component to choosing a VPS server hosting provider is deciding on the operating system (OS). There is a choice of two: Windows and Linux. Windows is a well-tried option. Linux, on the other hand, is an open source software that comes at a cheap price but is catching up with Windows in terms of capacity. It’s necessary to analyze which of the two best meets the given goals of the project and then decide on the OS.
Server configurations
When choosing a VPS plan, the server will be configured differently. It’s critical to understand how the server is configured since the speed and performance of the site depend on those configurations. First thing, the user needs to find out about the processor capacity, memory available, and allocated disk space. To ensure unbreakable traffic to a website, the server must have enough resources and be a powerful machine by itself. It should utilize the latest drives such as NVMe and be backed by Intel Xeon processors.
Time to go virtual with HostPro
To recap, VPS is a type of server that combines the qualities of shared hosting and a dedicated server. VPS creates an advanced system for users letting web hosts place multiple websites in isolation from one another. Thus, each site has its own virtual compartment and a share of resources no other website has access to.
To choose a VPS server hosting provider, you must look into server configurations and operating systems as well as the frequency of backups and uptime. You should be provided 24/7 support and decide whether you opt for managing the server yourself. If not, then surely you need a web host. We’d be happy to partner with you and create an unsurpassed hosting environment for you so contact us to discuss all the details.